Smart Scanning
Introducing the latest technology in soil analysis.

Making Every Hectare Reach Its Full Potential
A profitable precision farming program is based on an accurate understanding of the soil. The soil properties with the largest effect on productivity are those determining the amount of water and nutrients the crop will have available. Soil texture – the amount of sand, silt and clay is a major driver, along with soil organic matter and field topography. Soil pH, especially if it is outside the optimal range for the crop, will play a big role in nutrient availability.
To manage crop inputs, soil properties must be mapped precisely. Outdated and broad scaled soil surveys are likely to cause costly errors, especially when varying seed population, nitrogen or water.
Grid sampling, unless done on a quarter acre scale, doesn’t come close to the precision needed or what modern planting and fertilising equipment can achieve. The only affordable and precise option is on-the-go soil sensing.
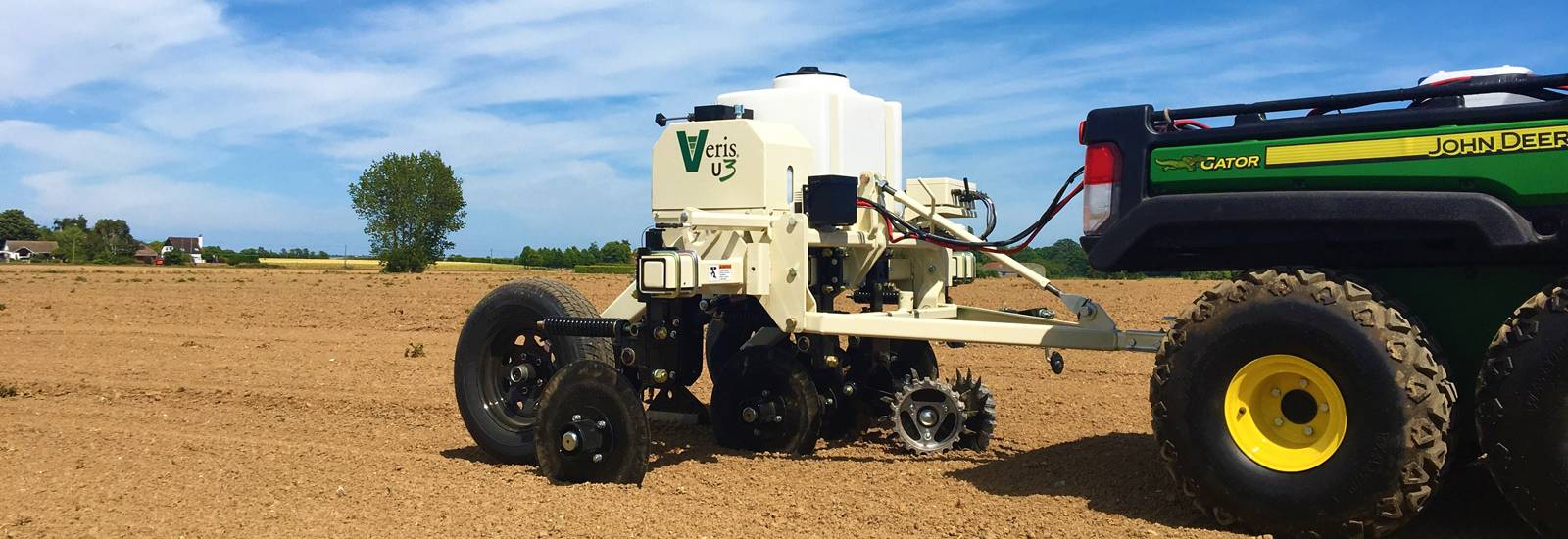
ACS Farm Image are now able to provide this through the latest technology in field scanning using the UK’s first Veris U3 in field scanner imported from Veris Technologies.
Mapping your field’s major physical, biological and chemical properties: pH, Organic Matter, Electrical Conductivity and Topography to help you manage each hectare to its full potential. The new soil sensor solution is designed to help increase profitability by removing errors in alternative precision management zones.

pH
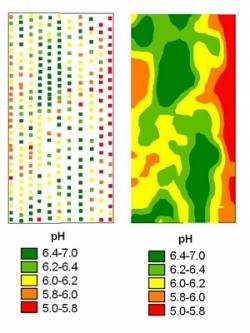
Soil pH has a significant impact on nutrient availability, microbial activity, nematode populations, soil herbicide efficacy and much more.
Soil pH is mapped using the Farm Image Smart Scanner’s in-field sensing with ruggedized pH electrodes. The result? More samples per hectare and a better return on lime investments.
Smart Scanner pH map
Organic Matter
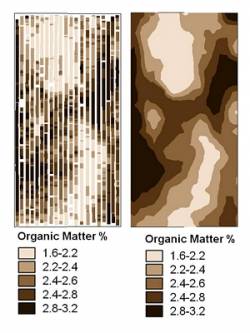
Soil Organic Matter (OM) is a critical soil property. Each % of OM can hold over 94,000 litres of water/ac and mineralise 9-18 kgs/ac of nitrogen. Because it is formed slowly over time, it is an excellent indicator of historic soil productivity.
‘Every 1% difference in organic matter results in over 94,000 litres of available soil water per acre.’
Soil Organic Matter is mapped using the Smart Scanner’s infrared soil optics. Darker soils contain more organic matter than lighter soils. The Smart Scanner measures below the soil surface to help ensure accurate readings. Sensor quality is high, with over 80 scans per acre and zones of contrasting soils are clearly evident.
Smart OM map
Using the Smart Scanner’s OM maps:
Farm Image’s OM Smart Map can be used in many ways including the following:
- Variable seeding
- Improved nitrogen management
- Variable irrigation
- Variable soil herbicides
- Site-specific gypsum as well as other applications
- Yield and crop image interpretation
- Directed manure applications
‘Each 1% of organic matter mineralizes 20-40 lbs of N/ac. Crediting soil organic matter for nitrogen can lead to added profit of $18.75/ac’
University of Nebraska
Soil Texture (EC)
‘Soil electrical conductivity has quickly become a favourite tool in mapping soil variability with fields’
Agronomy Journal 2003
The Farm Image Smart Scanner maps soil texture by analysing soil electrical conductivity (EC). Fine-textured soils conduct better than coarser soils. Proven EC arrays penetrate throughout the rooting zone.
Smart EC map
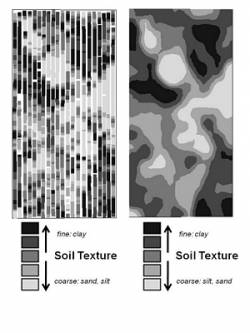
Soil texture- the amount of sand-silt-clay- is directly related to water holding capacity, nitrogen use and loss, and is the primary driver of productivity. Farm Image EC Smart Maps can be used for zone sampling, variable seeding, improved nitrogen management, variable irrigation, variable soil herbicides, salinity remediation and more.
Topography
The lay of the land affects water infiltration, drainage, nitrogen and soil loss. Severely sloping soil can exhibit reduced productive potential, often due to topsoil loss. Concave, or bowl-shaped areas can be poorly drained, especially if they also contain clay soils.
Topography is one of the most visible field properties and should be included with soil data in many variable rate applications, especially those involving water and nitrogen.
‘Topographical data in combination with soil information are useful for explaining yield variability on an agricultural field scale’
Plant, Soil and Environment 2008
Topography and Curvature Smart Maps
Farm Image Smart Fusion Maps
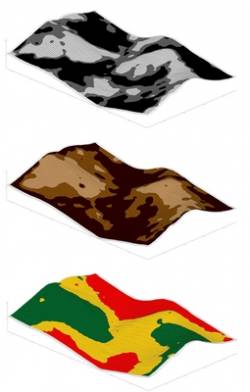
The Farm Image Smart Scanner shows its full worth in its ability to offer specific fusion maps for the following purposes:
PrecisionSampling- fusing Soil EC, OM and Topography into appropriately sized zones for soil sampling. The algorithm examines the variability found in soil EC, OM, as well as field slope and curvature in order to generate zones that capture the most significant soil variations. The resulting zones contain unique yield environments And are ideal for nutrient management such a P and K. Smart Precision Sampling Map
PrecisionSeed- fusing Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) readings with OM into appropriately-sized zones for variable seeding. The algorithm generates zones that contain unique soil combinations- an ideal map for creating seed population prescriptions. Smart Precision Seed Map
PrecisionSeed- T- fusing CEC, OM and topography into appropriately-sized zones for variable seeding. For example, depressional areas with heavy clay soil could receive higher seed rates in anticipation of emergence issues. Or eroded side slopes where top soil is thin could receive and even lower seed population than where that soil type lies on flatter ground. Smart Precision Seed T Map
iNseason Sampling- fusing soil EC , OM and topography into loss risk zones for nitrogen soil scouting sampling. The algorithm identifies the areas most susceptible to various causes of N loss. The resulting zones contain unique nitrogen activity environments and are ideal for improving N management. Samrt iNseason Sampling Map
PrecisionpH-IDC- fusing soil pH, EC, OM and topography into risk zones for iron deficiency chlorosis (IDC). IDC can cause significant yield loss in high pH, heavy clay soils in depressional areas due to lack of plant available iron. Applications of chelated iron can prevent this yield-robbing condition but can waste money when applied to areas of non IDC risk. The algorithm identifies the areas most susceptible to IDC and ranks them for levels of IDC risk. Smart PrecisionpH-IDC Map
Precision Pays!
Savings potential: immediate reduction in expenses
A single blanket rate applies inputs where they are not needed. For each of the variable management strategies outlined, variable rate lime, seed and nitrogen, there is money to be saved by applying inputs at the correct rate and in the right place. Lime won’t pay when soils are already above 6.5 pH. Overpopulating lower productivity soils wastes expensive seed. Blanket applying high nitrogen rates to higher OM soils, is not only a waste of money, but may also cause significant environmental harm.
Profit potential: Savings + Increased Yield
In addition to the savings potential, applying the correct amount of lime and challenging more productive soils with higher populations will likely lead to improved yields.
Farm Image News
Maize Maze Marking
It's rapidly approaching that time of year when Farm Image will be working on Maize Mazes, so why not give us a call to see how we can help
Happy Birthday Farm Image! 20 years of Agricultural Business Celebrated in this month’s South East Farmer
Our lovely team at Farm Image will be gracing farmer’s coffee tables across the region this month with a 5-page feature in South East Farmer to mark 20 years of...
Introducing SoilSolutions! Farm Image launch a brand-new range of soil conditioning products to tackle any nutrient deficiencies, improve yield and boost profit!
With Farm Image’s 20 years’ experience in identifying specific soil issues, and with 2017 seeing the introduction of our most accurate analysis service to date, the requirement as a company...
Farm Image Testimonials
“As a salad grower at Vitacress in Kent, our crop relies heavily on regular cultivation to maintain a high turnover rate. This demands constant PH correction of soil within a...
J. Wrighton, Vitacress, Kent
“Farm Image provided me with a specifically intensive precision soil sampling service at my request and convenience that allowed me to identify and neutralise the yield-limiting areas of land that...
M. Mayes, Kent - Salad Grower- Ickham, Kent
“We use ACS Farm Image every year to mark out our summer Maize Maze attraction due to their continued professionalism and ability to work around our busy farming schedule. They...
Quex Park Estates, Kent




